Malonic Acid
Product Details:
- Storage Store in cool, dry place, keep container tightly closed
- EINECS No 205-503-0
- Molecular Formula C3H4O4
- Shelf Life 24 months (under recommended storage)
- CAS No 141-82-2
- Shape Crystalline/Granular
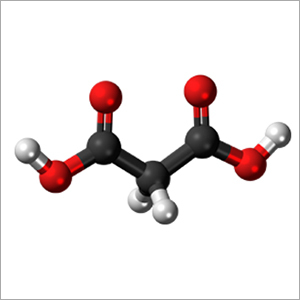
- Structural Formula HOOC-CH2-COOH
- Click to View more
Malonic Acid Price And Quantity
- 1 INR/Kilograms
- 1 Kilograms
Malonic Acid Product Specifications
- Intermediate in synthesis of barbiturates, vitamins, pharmaceuticals; laboratory reagent
- Odorless
- Sour
- Powder
- 135-137C
- White powder or crystalline
- 1.5 (0.1M solution)
- Malonic Acid (Propanedioic Acid)
- Industrial Grade, Laboratory Grade
- White crystalline solid, dicarboxylic acid, non-flammable, moderate toxicity, stable under normal conditions
- Used in organic synthesis, pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, flavors and fragrances, research
- Organic Acid
- 99% Min.
- C3H4O4
- 205-503-0
- Store in cool, dry place, keep container tightly closed
- Crystalline/Granular
- HOOC-CH2-COOH
- 141-82-2
- 24 months (under recommended storage)
- Moderately toxic if ingested
- Soluble in water, alcohol, ether, acetone
- 29171990
- 104.06 g/mol
- 1.60 Gram per cubic centimeter(g/cm3)
Malonic Acid Trade Information
- 25 Kilograms Per Week
- 3-4 Week
Product Description
Malonic Acid
| Analysis Item | Specification |
|---|---|
| Purity | 99% Min |
| Loss on Drying | 0.5% Max |
| Chloride(C1) | 0.02% Max |
| Sulfate(SO4) | 0.10% Max |
| Ignition Residue | 0.1% Max |
| Melting PointoC | 131.5 137.0 |
| Appearance | White Crystal Powder |
Applications of Malonic Acid
It is used in a number of manufacturing processes as a high value specialty chemical including the electronics industry, flavors and fragrances industry, specialty solvents, polymer crosslinking, and pharmaceutical industry. In 2004, annual global production of malonic acid and related diesters was over 20,000 metric tons.[15] Potential growth of these markets could result from advances in industrial biotechnology that seeks to displace petroleum-based chemicals in industrial applications.
Versatile Applications in Industry and Research
Malonic Acid is employed as an intermediate in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals, vitamins, barbiturates, and a variety of agrochemical products. Researchers value its reactivity in creating flavors, fragrances, and innovative organic compounds. The compounds stability and solubility in common solvents enhance its practical utility across laboratories and manufacturing units alike.
Safe Handling and Storage Guidelines
This substance is moderately harmful if ingested and can cause serious eye irritation. Always wear personal protective gear and avoid contact through inhalation, ingestion, or skin exposure. Store Malonic Acid in a tightly sealed container, placed in a cool, dry environment to maintain a shelf life of up to 24 months. Proper handling ensures safety and preserves chemical quality.
FAQs of Malonic Acid:
Q: How should Malonic Acid be handled safely in the laboratory or workplace?
A: Always wear suitable personal protective equipment such as gloves and safety goggles, and ensure proper ventilation. Avoid inhaling dust, ingestion, or direct contact with skin and eyes, as Malonic Acid is moderately toxic if swallowed and can cause serious eye irritation.Q: What are the primary uses and benefits of Malonic Acid in various industries?
A: Malonic Acid is vital as an intermediate in synthesizing pharmaceuticals, barbiturates, vitamins, agrochemicals, and research compounds. Its reactivity and solubility make it valuable for creating a wide array of products, contributing to advancements in organic synthesis and chemical manufacturing.Q: When and where should Malonic Acid be stored to maintain its stability and effectiveness?
A: Store Malonic Acid in a tightly closed container in a cool, dry place away from bases, oxidizers, and reducing agents. Under recommended storage conditions, it remains stable and retains its quality for up to 24 months.Q: What processes involve the use of Malonic Acid in organic synthesis applications?
A: Malonic Acid is commonly used for malonic ester synthesis, in the creation of substituted acetic acids, and as a precursor for pharmaceuticals. It also serves in laboratory procedures requiring pH adjustments or as a reagent in deprotonation reactions.Q: Where does Malonic Acid show compatibility or incompatibility regarding chemical reactions?
A: Malonic Acid is compatible with many solvents such as water, alcohol, ether, and acetone. However, it should be kept away from bases, oxidizers, and reducing agents, as these can trigger hazardous reactions and compromise its stability.Q: What are the transport and hazard specifications for Malonic Acid?
A: Malonic Acid is classified under UN 3261, hazard class 8 (corrosive), and belongs to packing group III for transport. While it is non-flammable, it poses risks if swallowed or if it contacts eyes, so it must be handled and transported with care.
Price:
- 50
- 100
- 200
- 250
- 500
- 1000+
Other Products in 'Speciality Chemical' category
 |
SHILPA CHEMSPEC INTERNATIONAL PRIVATE LIMITED
All Rights Reserved.(Terms of Use) Developed and Managed by Infocom Network Private Limited. |